
Gaussian 16 是 Gaussian 系列电子结构程序的最新版本,被全世界的化学家、化学工程师、生物化学家、物理学家和其他科学家使用。Gaussian 16 提供了一系列先进的建模功能。您可以使用它来研究您感兴趣的现实世界化学问题,即使是在普通的计算机硬件上,也可以解决它们的复杂性。
● Gaussian 16 可生成准确、可靠且完整的模型,无需偷工减料。
● 多种方法使 Gaussian 16 适用于各种化学条件、问题规模和化合物。
● Gaussian 16 在单 CPU、多处理器和多核、集群/网络和 GPU 计算环境中提供最先进的性能。
● 设置计算简单明了,甚至复杂的技术也是完全自动化的。灵活、易于使用的选项使您可以在需要时完全控制计算细节。
● 计算结果通过GaussView 6以自然直观的图形形式呈现。
Gaussian 16 从量子力学的基本定律出发,预测了各种化学环境中化合物和反应的能量、分子结构、振动频率和分子性质。Gaussian 16 模型可应用于稳定物质和难以或不可能通过实验观察的化合物,无论是由于其性质(例如毒性、可燃性、放射性)还是其固有的短暂性质(例如短命中间体和过渡结构)。
使用 Gaussian 16,您可以彻底研究您感兴趣的化学问题。例如,您不仅可以快速可靠地最小化分子结构,还可以预测过渡态的结构,并验证预测的驻点实际上是最小值或过渡结构(视情况而定)。您可以按照固有反应坐标 (IRC) 继续计算反应路径,并确定哪些反应物和产物通过给定的过渡结构连接。一旦您全面了解了势能面,就可以准确预测反应能量和势垒。您还可以预测各种化学性质。
● Molecular mechanicsEGF: Amber, UFF, Dreiding
● Semi-empirical methodsEGF†: AM1, PM6, PM7, DFTB, among others
● Hartree-FockEGF
● Density functional (DFT) methodsEGF, with support for a plethora of published functionals; long-range and empirical dispersion corrections are available where defined
● Complete active space self-consistent field (CASSCF)EGF, including RAS support and conical intersection optimizations
● Møller-Plesset perturbation theory: MP2EGF, MP3EG, MP4(SDQ)EG, MP4(SDTQ)E, MP5E
● Coupled cluster: CCDEG, CCSDEG, CCSD(T)E
● Brueckner doubles: BDEG, BD(T)E
● Outer Valence Green’s Function (OVGF): ionization potentials and electron affinities
● High accuracy energy models: G1-G4, CBS series and W1 series, all with variants
● Excited state methods: TD-DFTEGF, EOM-CCSDEG and SAC-CIEG
EEnergies; GAnalytic gradients; FAnalytic frequencies; F†Reimplemented with analytic frequencies.
A wide range of Gaussian results can be examined with GaussView’s visualization capabilities:
● Molecule annotations and/or property-specific coloring: e.g., atomic charges, bond orders, NMR chemical shifts
● Plots, including NMR, vibrational and vibronic spectra
● Surfaces or contours: e.g., molecular orbitals, electron density, spin density. Properties such as the electrostatic potential can be visualized as a colorized density surface.
● Animations: e.g., normal modes, IRC paths, geometry optimizations
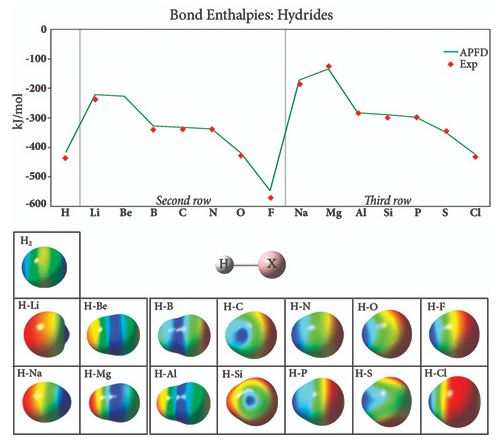
This graph plots the bond strength in second and third row hydride compounds (experiment: [CRC00]), which generally increases across the periodic table, with the strongest bond occurring in the element just before the noble gas. The plot has a similar overall shape for both rows, but the values for the third row are higher, due to the additional shielding from the nucleus by the filled second shell. The images show the electrostatic potential for each compound mapped onto an isodensity surface. The H2 surface illustrates the covalent nature of this bond; the bonds in the other hydride compounds are ionic. The negative electrostatic potential (red) is localized on the hydrogen atom at the beginning of each row, and it moves to the substituent as the atomic number increases within a row. Thus, hydride bond strengths increase across a period (row) and decrease as you go down a group (column), due to changes in electronegativity.
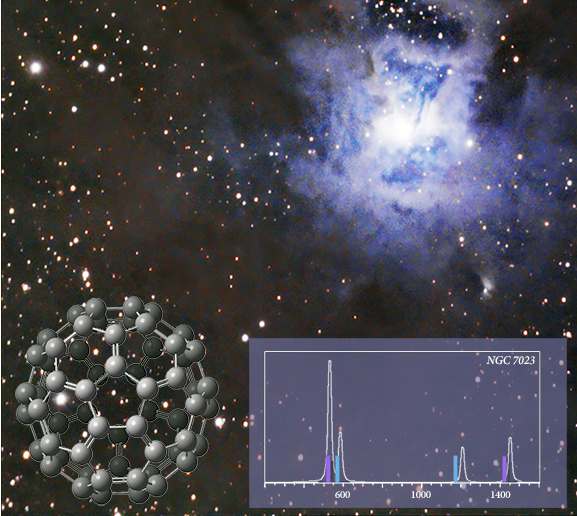
C60 was detected in IR observations of the Iris nebula (NGC 7023) in 2004 [Werner04, Sellgren10]. The inset graph shows the peak locations identified from the data (solid bars) superimposed on the spectrum predicted by the APFD/6-311+G(2d,p) model chemistry. The strongest peaks (purple) differ from the laboratory IR spectrum by 0.03-0.06 μm.
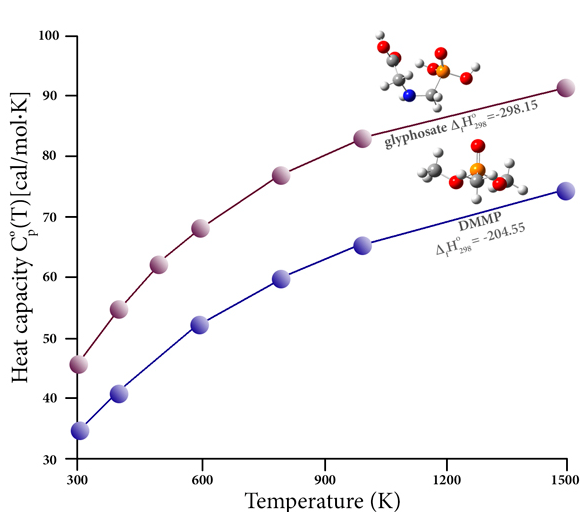
Organophosphorous compounds are commonly used as pesticides (among many other applications). These compounds adversely affect human health, due to both their inherent toxicity and from the harmful products created during combustion (e.g., as a result of burning previously-treated plant material). The decomposition of these compounds is difficult to study experimentally; thermochemical data for them is scarce. However, high accuracy thermochemistry predictions can bridge this gap and allow the thermal stability of the relevant compounds and combustion products to be studied. For example, this graph plots the heat capacity as a function of temperature for two such compounds: the pesticide glyphosate and the more benign flame retardant compound dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP). It also reports their heats of formation (kcal/mol), as predicted by the CBS-QB3 calculations of Khalfa and coworkers [Khalfa15]. Their paper presents computed results for a large number of trivalent and pentavalent phosphorus compounds, data which enables them to propose 83 original groups for use in the semi-empirical group contribution method of Benson, and thereby allows them to evaluate the thermochemical properties of some common pesticides, herbicides and related compounds.